Imagine that in the near future a patient needing surgery will swallow a small mobile robot that can autonomously perform the procedure without any external incisions or pain. Such robots have the potential to make state-of-the-art surgical concepts a reality by providing an unconstrained mobile platform to visualize, manipulate and surgically treat tissue. The project’s strategy will also harness the excitement surrounding robotics and computer science, and leverage it with the Investigators’ exceptional infrastructure for education innovation and outreach to provide new, inspirational educational experiences for students. Finally, the project outcomes can broadly impact a number of other areas that would benefit from the developed novel methodologies, including search and rescue, construction and maintenance, and remote imaging, where the environment is dynamic or changes upon repeated inspection.
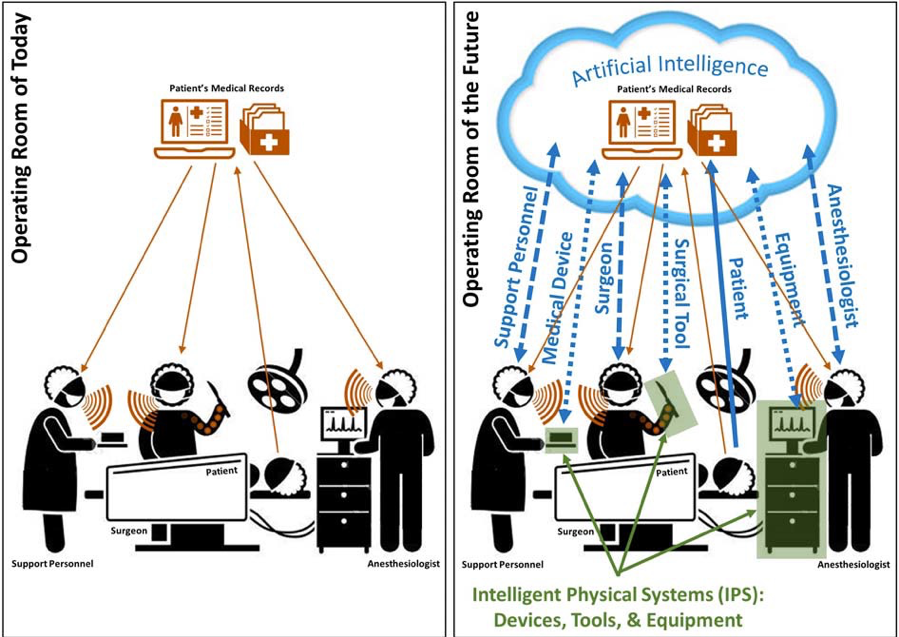
Figure 1: The stark difference between today’s operating room (left), and how Intelligent Physical Systems (IPS), that include medical devices, surgical tools and support equipment, could transform medical care and the operating room of the future (right).
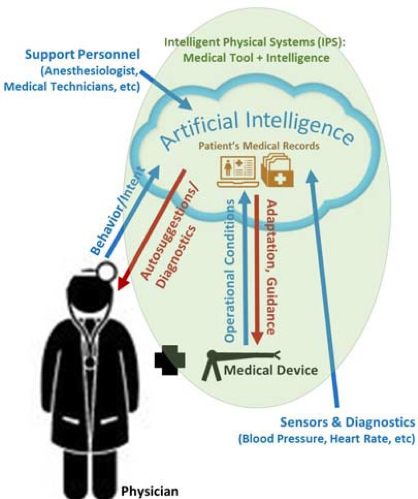
Intelligent Physical Systems (IPS), that include medical devices, surgical tools and support equipment, could transform medical care and the operating room of the future (right). The goal of this project is to gain a fundamental understanding of the cognition and adaptation needs of an intelligence-driven patient care approach to reduce medical errors. Realizing such an intelligent physical system would allow for augmenting physician capabilities. If one considers an operating room of the future, one can imagine scenarios where data is collected from, and shared with, all medical personnel including the surgeon, the supporting medical technicians, and anesthesiologists. In addition, artificial intelligence could be harnessed to look for unseen patterns in patient care. This operating room of the future will only be possible by establishing a new paradigm that includes medical devices with embedded smart and autonomous features. Such an intelligent physical system would gather knowledge from support personnel, sensors and diagnostics, and interpret physician intent and provide suggestions and diagnostic feedback in real-time. To provide real-world evaluation of this approach, the project will focus on robotic capsule endoscopy, with an intent to have immediate impact in conventional gastroenterology procedures. In pursuit of this goal, three research objectives are proposed: the first objective focuses on robotic capsule endoscopy perception and control; the second objective formulates the perception and diagnostic support requirements to augment physician performance; and the third objective integrates multimodal, multi-label, temporal data analytics for intelligent physician support.